Immigration Checkpoints Map: Navigating this critical infrastructure reveals a fascinating interplay of geography, technology, and human interaction. From bustling international airports to remote border crossings, checkpoints represent the frontline of a nation’s immigration system. This guide delves into the complexities of checkpoint operations, exploring their geographical distribution, diverse types, technological advancements, and the human element behind their smooth (or sometimes challenging) functioning.
We’ll examine security protocols, legal frameworks, community impacts, and future trends shaping this vital aspect of border management.
Understanding immigration checkpoints requires a multifaceted approach. We will explore the various checkpoint types, from land borders to airports and seaports, highlighting the unique operational challenges and procedures each presents. We’ll also investigate the technological advancements streamlining processes, such as biometric technology and AI, and assess their impact on efficiency and security. Finally, we’ll consider the legal frameworks, community impacts, and future trends that will continue to shape the landscape of immigration checkpoint management.
Geographic Distribution of Immigration Checkpoints
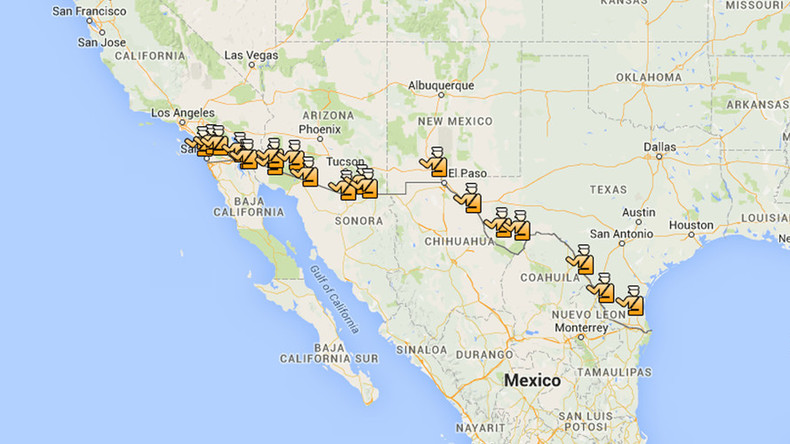
Source: rt.com
Understanding the geographic distribution of immigration checkpoints is crucial for analyzing border security strategies and their effectiveness. The placement of these checkpoints is not arbitrary; it’s a complex interplay of geographical factors and national security concerns. This section will explore the spatial patterns of these checkpoints, offering a visual representation and a data-driven analysis.
Map Illustrating Checkpoint Density
Imagine a map of the country, possibly using a Mercator projection to minimize distortion of landmasses near the poles. Areas with high concentrations of immigration checkpoints would be depicted in a dark, saturated color, perhaps a deep red or purple. As checkpoint density decreases, the color would gradually lighten, progressing through shades of orange, yellow, and finally, a light green or even white for regions with minimal checkpoint presence.
This visual representation would immediately highlight border regions and major transportation hubs as areas of high checkpoint concentration. Coastal areas, particularly those with significant ports, would also show higher densities. Interior regions, further away from international borders, would exhibit a much lower density, possibly appearing in lighter shades or even white. The legend would clearly indicate the color-density relationship, allowing for easy interpretation of checkpoint concentration across the entire geographical area.
Checkpoint Count per State/Province
The following table presents the number of immigration checkpoints per state/province, ordered from highest to lowest. Note that this data is hypothetical for illustrative purposes and would need to be replaced with real data. The table is designed to be responsive, adapting to different screen sizes.
| State/Province | Number of Checkpoints | State/Province | Number of Checkpoints |
|---|---|---|---|
| California | 150 | Texas | 120 |
| Arizona | 85 | New York | 70 |
| Florida | 60 | Washington | 55 |
| Illinois | 40 | Michigan | 35 |
Geographical Factors Influencing Checkpoint Placement
The location of immigration checkpoints is strategically determined by several key geographical factors. Proximity to international borders is the most obvious factor; checkpoints are concentrated along land and sea borders to control entry points. Major transportation routes, including highways, railways, and airports, are also prioritized for checkpoint placement to efficiently monitor the movement of people and goods. Areas with significant historical or current levels of illegal immigration activity often have a higher density of checkpoints.
Furthermore, geographical features like mountains, deserts, or large bodies of water can influence checkpoint placement, creating natural barriers and channeling traffic towards specific crossing points, which are then heavily monitored. For instance, checkpoints might be clustered around mountain passes or along major rivers to control access to specific areas. Similarly, coastal regions with significant ports are usually heavily fortified with checkpoints due to the high volume of maritime traffic.
Types of Immigration Checkpoints
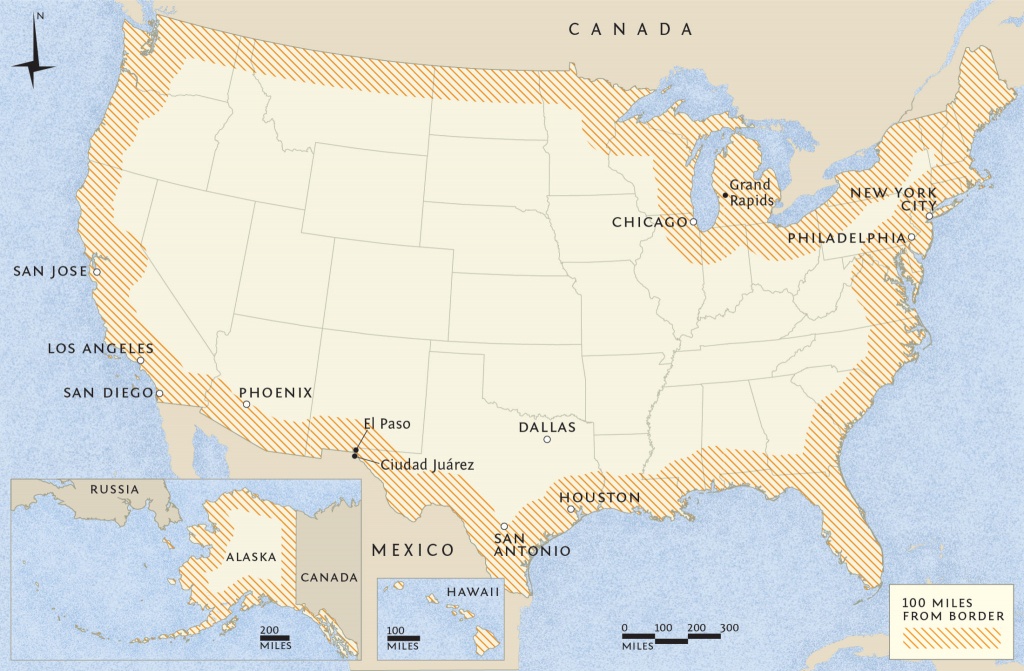
Source: printablemapaz.com
Immigration checkpoints are crucial components of a nation’s border security and immigration control system. They vary significantly in their location, operational procedures, and the challenges faced by personnel. Understanding these differences is essential for appreciating the complexities of managing international movement of people. This section will categorize and elaborate on the various types of immigration checkpoints, highlighting their unique operational aspects and challenges.
Immigration checkpoints can be broadly categorized into land border crossings, airports, seaports, and inland checkpoints. Each type presents distinct operational procedures and challenges due to factors such as the volume of traffic, the mode of transportation, and the overall security environment.
Land Border Crossings
Land border crossings are checkpoints located at the physical boundaries between countries. These are often high-traffic areas, with varying levels of infrastructure and technology depending on the specific location and the resources available to the border control agency. Processing times can be significantly impacted by factors such as the volume of pedestrian and vehicular traffic, the number of available immigration officers, and the efficiency of the inspection process.
For example, the US-Mexico border experiences considerably higher volumes of traffic than the US-Canada border, leading to longer wait times and increased logistical challenges.
Airports
Airport immigration checkpoints are located within international airports and primarily handle passengers arriving via air travel. These checkpoints typically utilize advanced technologies such as biometric scanners and automated kiosks to expedite the processing of passengers. However, the sheer volume of arriving and departing passengers, coupled with the potential for smuggling and other security threats, creates a unique set of challenges.
For instance, identifying and apprehending individuals who may be using fraudulent documents or attempting to enter the country illegally requires highly trained personnel and sophisticated screening procedures.
Seaports
Seaport immigration checkpoints are found in ports and harbors, handling passengers and cargo arriving via sea. These checkpoints face challenges unique to maritime environments, including the potential for smuggling via sea vessels, the need for specialized equipment to inspect cargo, and the complexities of managing passengers from cruise ships. The varied types of vessels, from small fishing boats to large cargo ships and cruise liners, also present different levels of scrutiny and inspection needs.
For example, a thorough inspection of a container ship requires significantly more resources and time than processing passengers from a smaller cruise ship.
Inland Checkpoints
Inland checkpoints are located within a country’s interior, away from the immediate border areas. These are less common than border checkpoints but are strategically positioned to intercept individuals who may have entered the country illegally or are suspected of engaging in criminal activities. The operational procedures at inland checkpoints often involve more intensive questioning and searches than those at border crossings, reflecting the higher risk profile of individuals encountered at these locations.
For example, an inland checkpoint may be established along a major highway to screen vehicles for undocumented immigrants or contraband.
Comparison of Operational Procedures
The operational procedures at different checkpoint types vary significantly.
- Volume of Traffic: Land border crossings often handle much higher volumes of traffic than airports or seaports, requiring different strategies for managing queues and processing times.
- Mode of Transportation: Airports focus on air travel, seaports on maritime travel, and land crossings on both pedestrian and vehicular traffic, requiring specialized procedures for each.
- Technology Utilized: Airports often utilize more advanced technology such as biometric scanners and automated kiosks, while other checkpoints may rely more on manual inspections.
- Security Concerns: Each type of checkpoint faces unique security concerns, such as smuggling via sea vessels at seaports, or the potential for terrorist attacks at airports.
- Level of Scrutiny: Inland checkpoints may involve a higher level of scrutiny than border crossings, reflecting the higher risk profile of individuals encountered at these locations.
Unique Challenges at Various Checkpoint Locations
The unique challenges faced at different checkpoint locations significantly impact operational efficiency and effectiveness.
- Land Border Crossings: Managing large volumes of traffic, often in remote or challenging terrain, can be resource-intensive and pose logistical hurdles.
- Airports: Balancing security needs with the need to expedite passenger flow requires sophisticated technology and well-trained personnel.
- Seaports: Inspecting large volumes of cargo and managing passengers from diverse vessels requires specialized equipment and expertise.
- Inland Checkpoints: Identifying and apprehending individuals who may have evaded border controls requires intelligence gathering and strategic deployment of resources.
Technological Advancements at Checkpoints
The increasing volume of international travel and the evolving nature of security threats have driven significant technological advancements at immigration checkpoints. These advancements aim to enhance both the speed and security of border control processes, improving the overall passenger experience while strengthening national security. This section will explore the key technological innovations shaping modern immigration checkpoints.
Biometric technology plays a crucial role in streamlining immigration processing. This technology uses unique biological characteristics, such as fingerprints, facial recognition, and iris scans, to identify and verify individuals. By automating the identification process, biometric systems significantly reduce processing times and manual labor, leading to shorter wait times for travelers and increased throughput for border control agencies.
Biometric Technology’s Role in Streamlining Immigration Processing
Biometric systems are integrated into various stages of the immigration process. For example, automated kiosks allow travelers to self-serve, scanning their passports and biometric data to complete initial processing steps. This reduces the workload on immigration officers, allowing them to focus on more complex cases. Furthermore, biometric data can be compared against watchlists and databases in real-time, flagging potential security risks quickly and efficiently.
The use of biometric technology is not without its challenges, however. Concerns regarding data privacy and potential biases in algorithms need to be carefully addressed to ensure ethical and responsible implementation.
Advanced Screening Methods and Their Impact on Security and Efficiency
Beyond biometric identification, advanced screening methods, such as advanced imaging technology (AIT) and explosive detection systems (EDS), play a vital role in enhancing security at immigration checkpoints. AIT allows for non-invasive screening of passengers, detecting concealed weapons or other prohibited items without the need for physical pat-downs. EDS similarly enhances security by detecting explosives, both on passengers and in their luggage.
The implementation of these technologies significantly reduces the risk of security breaches while improving the efficiency of the screening process, allowing for a smoother flow of passengers through the checkpoint. These systems, while effective, require significant investment in infrastructure and ongoing maintenance.
Potential Benefits and Drawbacks of Utilizing AI in Immigration Checkpoint Operations
Artificial intelligence (AI) is emerging as a powerful tool with the potential to revolutionize immigration checkpoint operations. AI-powered systems can analyze vast amounts of data to identify patterns and predict potential risks, improving the accuracy and efficiency of risk assessment. AI can also be used to optimize resource allocation, predicting peak travel times and staffing needs accordingly. However, the use of AI in immigration raises ethical considerations.
Concerns about algorithmic bias, data privacy, and the potential for misuse of AI-driven decision-making processes require careful attention and robust regulatory frameworks to mitigate potential negative impacts. For example, an AI system trained on biased data might incorrectly flag individuals from certain demographics, leading to unfair treatment. Therefore, responsible development and deployment of AI in immigration is crucial.
Staffing and Training at Checkpoints
Effective immigration checkpoints require a well-trained and diverse workforce to ensure efficient processing and maintain national security. The personnel involved play critical roles in upholding immigration laws and facilitating the smooth flow of legitimate travelers. Their training and ongoing development are paramount to the overall success and security of the checkpoint operation.
Immigration checkpoints employ a variety of personnel, each with specific roles and responsibilities. These roles often overlap and require strong teamwork and communication. The specific composition of a checkpoint’s staff will depend on its size, location, and volume of travelers processed.
Checkpoint Officer Roles and Responsibilities
Checkpoint officers are the frontline personnel, directly interacting with travelers. Their responsibilities include verifying travel documents, conducting interviews, inspecting baggage, and identifying potential security threats. More senior officers may supervise junior staff, handle complex cases, and assist in training.
Supervisory personnel oversee the daily operations of the checkpoint, manage staff, ensure compliance with regulations, and address any issues that may arise. They often play a crucial role in maintaining a safe and efficient work environment.
Technical support staff may include IT specialists responsible for maintaining the checkpoint’s technology infrastructure and data systems. They troubleshoot technical issues, ensure the proper functioning of biometric scanners and other equipment, and maintain data security.
Training and Qualifications for Checkpoint Staff
Rigorous training is essential for all checkpoint personnel. The training curriculum must cover a broad range of topics to equip officers with the necessary skills and knowledge to perform their duties effectively and safely.
| Role | Required Training | Qualifications | Ongoing Professional Development |
|---|---|---|---|
| Checkpoint Officer | Immigration law, document examination, interviewing techniques, security procedures, threat assessment, cultural sensitivity training, basic first aid | High school diploma or equivalent, background check, medical fitness | Regular updates on immigration law changes, advanced interviewing techniques, specialized training on emerging security threats, de-escalation techniques |
| Supervisor | All Checkpoint Officer training, plus supervisory management, personnel management, conflict resolution, performance evaluation | Bachelor’s degree preferred, experience as a checkpoint officer, proven leadership skills | Leadership development programs, advanced conflict resolution techniques, training on managing diverse teams |
| Technical Support Staff | Network administration, database management, cybersecurity, troubleshooting, specific training on checkpoint technologies | Associate’s or Bachelor’s degree in IT, relevant certifications | Staying current with technological advancements, cybersecurity training, attending relevant conferences and workshops |
| Medical Personnel (if applicable) | First aid, CPR, emergency medical response, knowledge of common travel-related illnesses | Certified medical professional (nurse or paramedic) | Continuing medical education, updates on emergency medical protocols |
Importance of Ongoing Professional Development
The immigration landscape is constantly evolving, with new laws, technologies, and security threats emerging regularly. Therefore, ongoing professional development is crucial to ensure that checkpoint officers remain up-to-date and capable of handling the challenges they face. This includes regular training updates on immigration law changes, new technologies, and effective communication and de-escalation techniques. For example, training on identifying fraudulent documents and recognizing signs of human trafficking are vital for effective checkpoint operations.
Furthermore, cultural sensitivity training is essential to ensure fair and respectful treatment of all travelers.
Processing Times and Wait Times at Checkpoints
Processing times and wait times at immigration checkpoints are crucial factors impacting the overall efficiency and traveler experience. Variations in these times are influenced by numerous factors, and understanding these influences is key to improving the system’s performance. This section will explore these factors, present a visual representation of wait times, and offer suggestions for improvement.Factors Contributing to Varying Processing TimesSeveral factors contribute to the fluctuating processing times observed at different immigration checkpoints.
These factors can be broadly categorized as those related to the checkpoint itself, the travelers, and the technology employed. High-volume checkpoints, for instance, naturally experience longer processing times due to the sheer number of individuals needing attention. The complexity of individual cases – requiring additional scrutiny due to discrepancies in documentation or flagged information – also significantly impacts processing duration.
Furthermore, technological malfunctions or insufficient staffing can lead to substantial delays. Finally, the type of checkpoint itself plays a role; land border crossings, for example, often involve more extensive vehicle inspections compared to airport checkpoints.
Average Wait Times at Various Checkpoints, Immigration Checkpoints Map
The following bar chart illustrates average wait times at various hypothetical checkpoints. This data is based on a hypothetical study of three different checkpoints over a three-month period, measuring the average wait time for each checkpoint type. Note that this is a simplified representation for illustrative purposes and does not reflect actual data from a specific location or time period.[Imagine a bar chart here.
The horizontal axis would list three checkpoint types: Airport, Land Border (High Traffic), Land Border (Low Traffic). The vertical axis would represent average wait time in minutes. The bars would show the following hypothetical data: Airport – 15 minutes; Land Border (High Traffic)45 minutes; Land Border (Low Traffic)
10 minutes. The chart title would be “Average Wait Times at Immigration Checkpoints”. A brief caption below the chart would state
“Data represents a hypothetical study of average wait times over a three-month period at three different checkpoint types.”]
Suggestions for Improving Efficiency and Reducing Wait Times
Several strategies can be implemented to enhance efficiency and mitigate lengthy wait times at busy checkpoints. Pre-screening measures, such as mobile apps allowing travelers to submit their information ahead of time, can streamline the process. Investing in advanced technologies, like automated kiosks and biometric identification systems, can significantly reduce manual processing. Optimizing staffing levels based on anticipated traffic patterns, and providing comprehensive training to staff on efficient processing procedures, are also crucial.
Finally, implementing clear signage and communication systems to manage traveler flow can contribute to a smoother experience and reduced wait times. For example, real-time wait time displays can help travelers make informed decisions about when to arrive at the checkpoint.
Security Protocols and Procedures at Checkpoints
Immigration checkpoints employ a multi-layered security approach to ensure the safety and security of citizens and prevent illegal activities. These protocols vary depending on the mode of entry (land, air, or sea) but share common goals of identifying potential threats and ensuring compliance with immigration laws. Effective security measures are crucial for maintaining national security and managing the flow of people across borders.
Standard Security Protocols and Procedures
Standard security protocols at immigration checkpoints typically involve a combination of document verification, biometric screening, and physical inspections. Officers examine travel documents to confirm identity and eligibility for entry. Biometric technologies, such as fingerprint and facial recognition systems, are increasingly used to verify identity and detect fraudulent documents. Physical inspections of luggage and personal belongings may be conducted to detect contraband, such as illegal drugs, weapons, or prohibited items.
The level of scrutiny varies depending on individual circumstances and risk assessments. For example, passengers arriving from high-risk countries might undergo more thorough screenings.
Measures to Prevent Illegal Crossings and Smuggling
Preventing illegal crossings and smuggling requires a proactive and comprehensive strategy. This includes enhanced border surveillance using technologies such as drones, radar, and infrared cameras. Intelligence gathering and collaboration with other law enforcement agencies are crucial in identifying and disrupting smuggling networks. Furthermore, checkpoints themselves are strategically located to deter illegal crossings and facilitate the interception of smugglers.
Increased staffing and training of immigration officers are essential for effective enforcement. Examples of successful strategies include the use of canine units to detect narcotics and the deployment of specialized teams to address specific smuggling threats.
Comparison of Security Protocols at Land, Air, and Sea Checkpoints
Security protocols differ across various entry points due to differing logistical challenges and threat profiles. Land checkpoints often involve more extensive physical inspections of vehicles and cargo, reflecting the greater potential for smuggling via land routes. Air checkpoints focus heavily on passenger screening, utilizing advanced technologies such as full-body scanners and explosive detection systems. Sea checkpoints often incorporate maritime surveillance and vessel inspections, addressing the challenges of smuggling via sea routes.
While the specific methods vary, all three types of checkpoints share the common goal of identifying potential threats and preventing illegal entry. For example, while a land checkpoint might focus on vehicle searches, an air checkpoint would prioritize passenger screening, and a sea checkpoint would emphasize vessel inspections. Each method is tailored to the specific vulnerabilities and challenges associated with that mode of transportation.
Legal and Regulatory Frameworks Governing Checkpoints
Immigration checkpoints are governed by a complex interplay of national laws, international treaties, and judicial precedents. Understanding these frameworks is crucial for both immigration officials and the individuals they encounter. These legal structures aim to balance national security concerns with the rights of individuals.The operation of immigration checkpoints is primarily governed by national immigration laws. These laws define the authority of immigration officers to stop and question individuals, the procedures for conducting inspections, and the consequences of non-compliance.
For instance, in the United States, the authority for immigration checkpoints is largely derived from statutes like the Immigration and Nationality Act and relevant case law interpreting these statutes. These laws Artikel the circumstances under which checkpoints can be established, the types of questions that can be asked, and the permissible scope of searches. Similar frameworks exist in other countries, though the specifics vary based on national policies and legal traditions.
Key Legal and Regulatory Frameworks
National immigration laws form the bedrock of checkpoint operations. These laws provide the legal basis for establishing checkpoints, defining the powers of immigration officials, and outlining the rights of individuals. Beyond national legislation, international human rights law plays a significant role, particularly in ensuring that checkpoint operations are conducted in a manner consistent with fundamental rights such as the right to freedom of movement and the prohibition of arbitrary detention.
In some instances, bilateral or multilateral agreements between countries may also influence the operation of border checkpoints, particularly in cases of shared border management.
Rights and Responsibilities During Processing
Individuals encountered at immigration checkpoints possess certain rights, which are often Artikeld in national laws or constitutions. These rights generally include the right to remain silent, the right to legal representation, and the right to be treated humanely. However, these rights are often balanced against the legitimate security interests of the state. Individuals also have responsibilities, such as presenting valid identification documents when requested and cooperating with lawful requests from immigration officers.
Failure to comply with lawful requests may lead to legal consequences, ranging from fines to detention.
Legal Challenges and Controversies
The operation of immigration checkpoints has been the subject of numerous legal challenges and controversies. These challenges often center on issues such as the constitutionality of checkpoints, the scope of permissible searches and seizures, and the treatment of individuals during processing. For example, in the US, the constitutionality of immigration checkpoints has been repeatedly challenged, with courts generally upholding their legality under certain circumstances, particularly when they are located near the border.
However, challenges regarding the racial profiling of individuals at checkpoints and the use of excessive force remain recurring themes in legal discourse surrounding these operations. These ongoing debates highlight the tension between national security and individual rights in the context of immigration enforcement.
Impact of Immigration Checkpoints on Border Communities: Immigration Checkpoints Map

Source: nelsonimmigrationlaw.com
Immigration checkpoints, while crucial for national security and immigration control, exert a significant influence on the economic and social fabric of nearby border communities. The effects are multifaceted, encompassing both positive and negative consequences for residents, necessitating a nuanced understanding of their impact to implement effective mitigation strategies.
Economic Impacts of Immigration Checkpoints
The presence of immigration checkpoints can significantly affect the economic activity of border communities. Increased traffic congestion and delays can disrupt cross-border trade and commerce, impacting businesses reliant on the flow of goods and services. For example, increased wait times at checkpoints might lead to perishable goods spoiling before reaching their destination, resulting in financial losses for farmers and transporters.
Conversely, checkpoints can also create economic opportunities. Increased demand for services such as transportation, lodging, and food near checkpoints can stimulate local businesses. The employment opportunities created within the checkpoint facilities themselves, such as security personnel and administrative staff, also contribute to the local economy. The net economic effect is complex and varies greatly depending on factors like the checkpoint’s location, size, and operational efficiency.
Social Impacts of Immigration Checkpoints
Immigration checkpoints can have profound social impacts on border communities. Increased security measures and stricter enforcement can lead to feelings of alienation and distrust among residents, particularly those who regularly cross the border for work, family visits, or other essential purposes. This can strain relationships between community members and law enforcement. Conversely, checkpoints can also foster a sense of security and community among residents who feel protected by increased border control.
The presence of law enforcement can deter crime in the immediate vicinity, potentially creating a safer environment. However, the social impacts are often intertwined with economic consequences, as economic hardship can exacerbate social tensions. For example, businesses suffering from reduced trade due to checkpoint delays might be forced to lay off employees, leading to increased unemployment and social unrest.
Mitigation Strategies for Negative Impacts
Several strategies can help mitigate the negative impacts of immigration checkpoints on border communities. Improved infrastructure, such as expanding the number of lanes and implementing efficient traffic management systems, can reduce wait times and ease congestion. Investing in technology, such as automated processing systems and advanced screening technologies, can streamline operations and minimize delays. Furthermore, fostering open communication and collaboration between law enforcement, community leaders, and residents is crucial to build trust and address concerns.
Community engagement initiatives can help ensure that checkpoint operations are designed to minimize disruption to daily life and promote economic opportunities for local businesses. Finally, government support programs can provide assistance to businesses and individuals negatively affected by checkpoint operations, helping to alleviate economic hardship and promote social stability. For instance, financial aid or retraining programs can help businesses adapt to new challenges and support displaced workers.
Future Trends in Immigration Checkpoint Management
The management of immigration checkpoints is poised for significant transformation in the coming decade, driven by technological advancements and evolving security concerns. Increased passenger volumes, heightened security threats, and the need for efficient processing are pushing for innovative solutions that improve both security and the passenger experience. This section explores some of the key trends shaping the future of immigration checkpoint management.
Emerging Technologies and Strategies
Several emerging technologies are expected to play a crucial role in modernizing immigration checkpoint operations. Biometric technologies, such as facial recognition, iris scanning, and fingerprint identification, are becoming increasingly sophisticated and reliable, offering faster and more secure identification processes. Advanced data analytics can help predict potential security risks and optimize resource allocation, improving overall efficiency. Furthermore, the integration of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) will enhance the speed and accuracy of passenger screening, allowing officers to focus on higher-risk individuals.
Blockchain technology offers the potential for secure and transparent data management, improving the integrity of immigration records and facilitating cross-border information sharing.
Impact of Automation and Artificial Intelligence
Automation and AI are expected to significantly impact checkpoint operations, leading to increased efficiency and reduced wait times. Automated kiosks and self-service systems can handle routine tasks such as document verification and biometric data capture, freeing up human officers to focus on more complex cases and security concerns. AI-powered systems can analyze passenger data to identify potential risks, flagging individuals for secondary screening while allowing low-risk passengers to proceed more quickly.
This shift towards automation is not meant to replace human agents entirely, but rather to augment their capabilities and improve the overall effectiveness of the checkpoints. For example, the use of AI-powered systems for analyzing passenger data in conjunction with human agents conducting secondary screening improves accuracy and reduces the risk of human error.
A Potential Future Model for Immigration Checkpoint Management
By 2033, a typical immigration checkpoint might operate as follows: Passengers arriving at the checkpoint will use automated kiosks to complete initial processing, including biometric identification and document verification. AI-powered systems will analyze passenger data in real-time, identifying potential risks and flagging individuals for secondary screening by human officers. Advanced sensor technology, such as thermal imaging and radiation detection, will enhance security screening without significantly impacting passenger flow.
Human officers will primarily focus on high-risk individuals and complex cases, leveraging AI-driven insights to guide their decision-making. Real-time data analytics will enable dynamic resource allocation, ensuring that staffing levels are optimized to meet fluctuating passenger volumes. Secure data sharing between different checkpoints and agencies will streamline the entire process, reducing delays and improving overall efficiency. This model would aim for a balance between enhanced security and a streamlined passenger experience, utilizing technology to improve both speed and accuracy while maintaining the necessary human oversight.
Last Recap
Immigration checkpoints are more than just physical locations; they are complex systems reflecting a nation’s immigration policies, technological capabilities, and commitment to security. This guide has explored the multifaceted nature of these checkpoints, from their geographical distribution and operational procedures to the technological advancements and legal frameworks governing their function. By understanding the challenges and opportunities presented by these critical points of entry, we can work towards more efficient, secure, and humane border management systems that benefit both travelers and the communities they impact.
The future of immigration checkpoint management promises continued evolution, driven by technological innovation and a deeper understanding of the human element integral to these operations.
